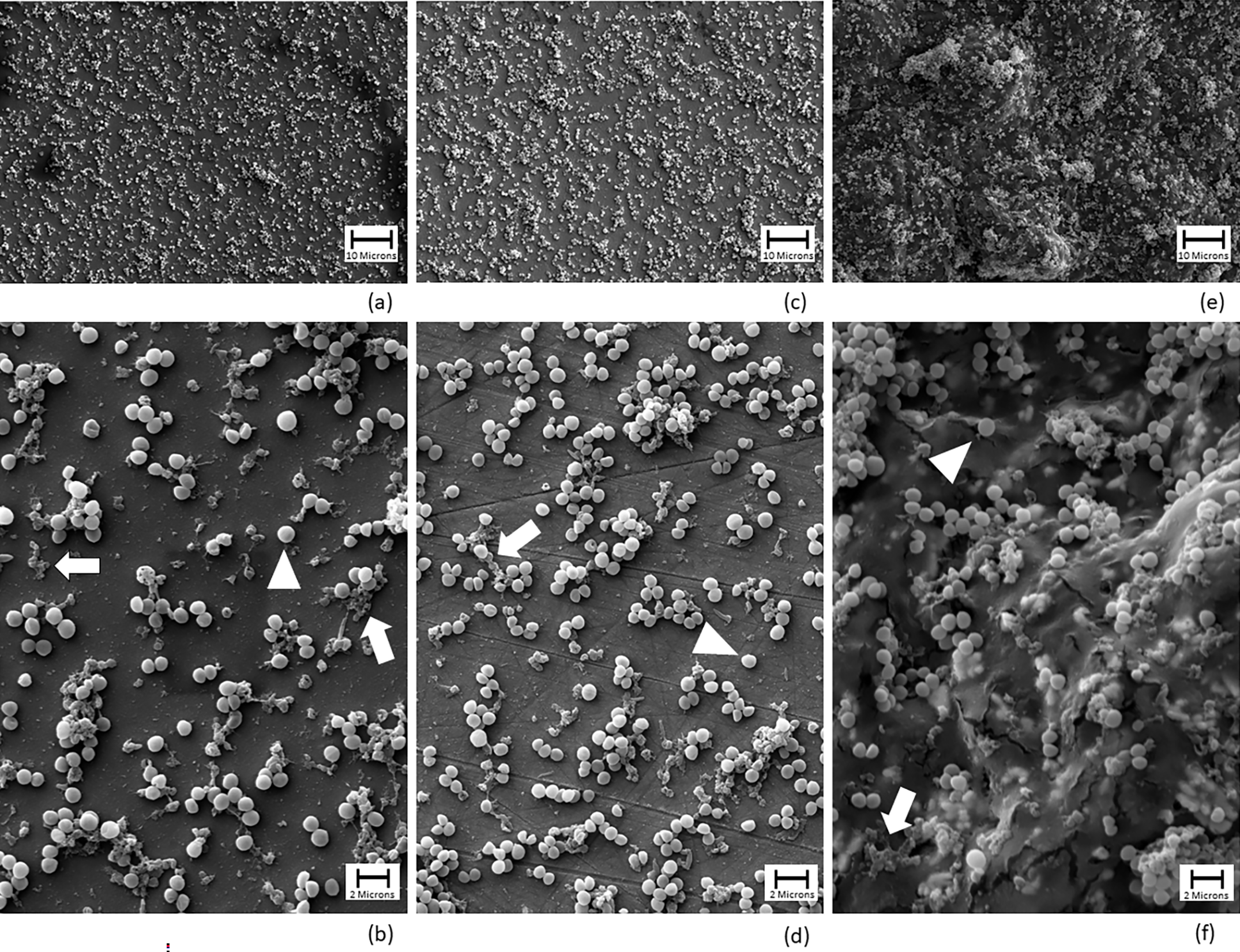
Antiseptic solutions are often used in total joint arthroplasty to help prevent or treat the challenging complication of periprosthetic joint infection. In a study now available in JBJS, Chao et al. evaluated the efficacy of several antiseptic solutions in eradicating methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) and Escherichia coli biofilms established in vitro on orthopaedic surfaces commonly used in total joint arthroplasty.
“Antiseptic solutions vary considerably in efficacy against bacterial biofilm,” the authors concluded. Access the study at JBJS.org:
The investigators compared 5 irrigation solutions: 10% povidone-iodine; a 1:1 mixture of 10% povidone-iodine and 3% hydrogen peroxide; diluted povidone-iodine; 0.05% chlorhexidine gluconate in sterile water; and a surfactant-based formulation of ethanol, acetic acid, sodium acetate, benzalkonium chloride, and water.
Three orthopaedic surfaces were tested: biofilms were grown on cobalt-chromium (CC), oxidized zirconium (OxZr), and polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) discs for 24 and 72 hours.
The primary outcome was determining which solutions achieved a 3-log (1,000-fold) reduction in bacterial colony-forming unit (CFU) counts compared with controls, a previously described threshold of clinical effectiveness against biofilm1.
Conclusions: “The 10% povidone-iodine solution with or without hydrogen peroxide consistently removed MSSA and E. coli biofilms on multiple orthopaedic surfaces,” the researchers found.
In discussing the findings of their experiments, they write that treatments with 10% povidone-iodine and 10% povidone-iodine and hydrogen peroxide (PI + HP) “had the greatest effect on reducing bacterial counts in both immature and mature biofilms after 3 minutes of exposure. These treatments completely eradicated bacteria from mature biofilm on CC and OxZr, whereas they reached clinical efficacy on PMMA … The 10% PI + HP consistently produced the largest reduction in CFU counts on all surfaces. In contrast, the other antiseptic solutions were either completely ineffective (chlorhexidine and diluted PI) or inconsistent (surfactant-based).”
Read the full study at JBJS.org: Not All Antiseptic Solutions Are Equivalent in Removing Biofilm. A Comparison Across Different Orthopaedic Surfaces
For more content exploring the treatment and prevention of infection in musculoskeletal care, go to: What’s Trending in Infection at JBJS.org
Related reading on OrthoBuzz:
Periprosthetic Joint Infection After Hip Replacement Linked to Increased Mortality
References:
- Premkumar A, Nishtala SN, Nguyen JT, Bostrom MPG, Carli AV. The AAHKS Best Podium Presentation Research Award: Comparing the efficacy of irrigation solutions on Staphylococcal biofilm formed on arthroplasty surfaces. J Arthroplasty. 2021 Jul;36(7S):S26-32.